Instructional Strategies
Table of Contents
- Lesson Organization
- Introduction
- Activate Attention (Focus Attention on Learning Activity)
- Establish Purpose (Inform Learner of the Lesson's Purpose)
- Arouse Interest and Motivation (Explain Importance &
Relevance of the Lesson to Learner)
- Preview Learning Activity (Provide Overview)
- Body
- Recall Relevant Prior Knowledge (Stimulate Recall of Prior
Knowledge)
- Process Information and Examples (Present Information and
Examples)
- Focus Attention (Gain and Direct Attention)
- Employ Learning Strategies (Guide or Prompt Use of Learning
Strategies
- Practice (Provide For and Guide Practice)
- Evaluate Feedback (Provide Feedback)
- Conclusion
- Summarize and Review (Provide Summary and Review)
- Transfer Learning (Enhance Transfer)
- Re-motivate and Close (Provide Remediation and Closure)
- Assessment
- Assess Learning (Conduct Assessment)
- Evaluate Feedback (Provide Feedback and Remediation)
- 9 Events of Instruction (Gagnè, 1972)
- Gaining Attention
- Informing the learner of the objective
- Stimulating recall of prerequisite learning
- Presenting stimulus materials
- Providing learning guidance
- Eliciting performance
- Providing feedback
- Assessing performance
- Enhancing retention and transfer
- Cognitive Processing Activities
- Attending
- Goal
- Motivation
- Orientation
- Prior Learning
- Processing Information
- Focusing Attention
- Learning Strategies (Cognitive Strategies)(Reiguluth, 1983)
- Practice
- Feedback
- Consolidation
- Transfer
- Remotivation
- Assessment
- Feedback
- Microstrategies (Dick & Carey, 2005, p. 183)
- Group discussions
- Independent Reading
- Case Studies
- Lectures
- Computer Simulations
- Worksheets
- Cooperative Group projects
Introduction
There are three types of strategies within instructional design theories
(Reigeluth, 1983)
- Organizational strategies are broken down into micro and macro
levels and deal with the way in which a lesson is arranged and
sequenced.
- Delivery strategies are concerned witht he decisions that affect the
way in which information is carried to the student, particularly the
selection of instructional media.
- Management strategies involve the decisions that help the learner
interact with the activities designed for learning.
Lesson Organization
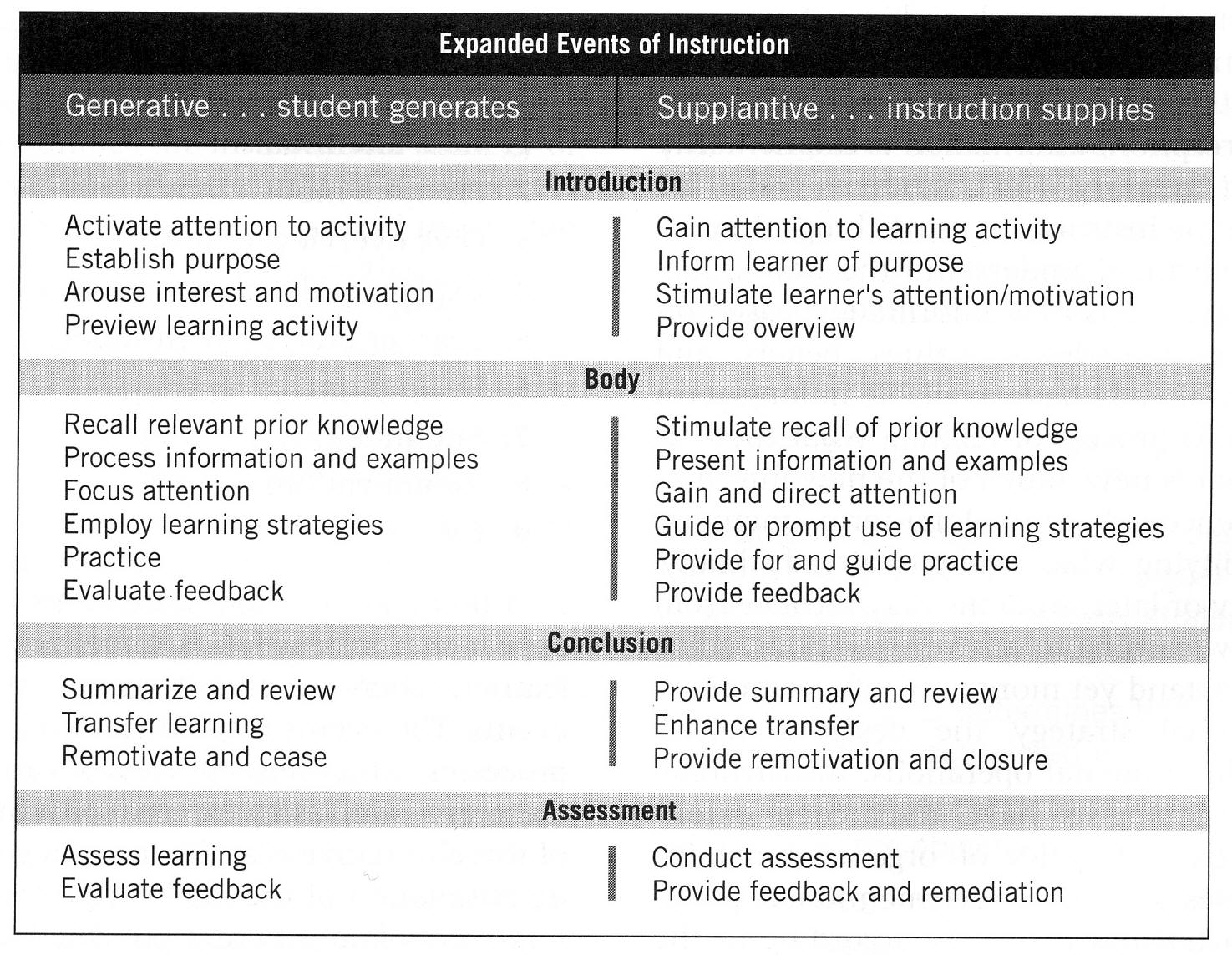 Expanded Events of
Instruction; (Smith & Ragan, 2005, p. 130)
Expanded Events of
Instruction; (Smith & Ragan, 2005, p. 130)
Introduction
Activate Attention
"The purpose of this event is for learners to focus their attention on
the learning task" (Smith & Ragan, 2005, p. 131).
Establish Purpose
"Knowing the learning goal can establish an expectancy in learners,
arousing their interest and giving them a goal toward which to direct their
cognitive energies" (Smith & Ragan, 2005, p. 132).
Arouse Interest and Motivation
"The critical aspect of this part of the introduction is that learners
are cognizant of the importance and relevance of the lesson and/or
encouraged to explore the personal relevance of the lesson (Smith and Ragan,
2005, p. 133).
Preview Learning Activity (Provide Overview)
Example: A content outline (highly supplantive).
Body
Recall Relevant Prior Knowledge
Learners are stimulated to recall prior knowledge from long term memory
which will be helpful in learning the new objective.
Process Information and Examples (Present Information and Examples)
"During this event learners encounter the material they will be
learning. This information may be presented in a expository (didactic)
form in which generalities such as concept definitions or statements of
generalizations are presented prior to their examples. The sequence may
instead involve more discovery (inquiry), in which the learners are
presented with examples of the concepts or applications of principles
and are encouraged to induce the generality" (Smith & Ragan, 2005, p.
134).
Focus Attention (Gain and Direct Attention)
"Although the learner's attention was invoked at the beginning of
instruction, it must be refocused continuously throughout the lesson"
(Smith & Ragan, 2005, p. 135).
Employ Learning Strategies (Guide or Prompt use of Learning
Strategies)
"The purpose of this event is to assist learners to use effective
strategies, and that purpose is essentially accomplished by prompting
learners to use appropriate learning strategies" (Smith & Ragan, 2005,
p. 135).
- Basic Rehearsal Strategies
- Repeating the names of items in an ordered list like the
order of the planets in the solar system.
- Complex Rehearsal Strategies
- Used when the to be learned material is prose, such as a
lesson from a science textbook
- Repeating the material aloud (i.e., shadowing)
- Copying the material
- Taking verbatim notes
- Underlining important parts of the material
- Basic Elaboration Strategies
- Complex Elaboration Strategies
- Basic Organizational Strategies
- Complex Organizational Strategies
- Comprehension Monitoring Strategies
- Affective and Motivational Strategies
Practice (Provide For and Guide Practice)
Evaluate Feedback (Provide Feedback)
Conclusion
Summarize and Review (Provide Summary and Review)
Remotivate and Close (Provide Remediation and Closure)
Assessment
Assess Learning (Conduct Assessment)
Evaluate Feedback and Seek Remediation (Provide Feedback and
Remediation)


9 Events of Instruction (Gagné)
- Gaining Attention
- Informing the learner of the objective
- Stimulating recall of prerequisite learning
- Presenting stimulus materials
- Providing learning guidance
- Eliciting performance
- Providing feedback
- Assessing performance
- Enhancing retention and transfer
Cognitive Processing Activities
- Attending
- Goal
- Motivation
- Orientation
- Prior Learning
- Processing Information
- Focusing Attention
- Learning Strategies (Cognitive Strategies)(Reiguluth, 1983)
- Practice
- Feedback
- Consolidation
- Transfer
- Remotivation
- Assessment
- Feedback
Microstrategies
- Group discussions
- Independent Reading
- Case Studies
- Lectures
- Computer Simulations
- Worksheets
- Cooperative Group projects